Phishing is a social engineering attack which is an attempt to steal sensitive and personal user information with the ill intents of gaining illegal access or financial gains. The stolen information can be in the form of usernames, passwords, bank account details or credit card numbers.
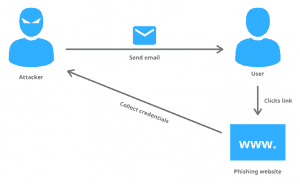
The attackers utilize this information in two ways: either they sell the information to 3rd parties or use for their ill purposes i.e. identity theft or illegal access to your bank accounts. According to reports, phishing attempts have grown 65% in the last year.
The attacker carries out the phishing attack by masquerading as a reputable source and luring the victim to click on suspicious links. There are various types of phishing:
- Spear Phishing – This method is used to steal data for malicious purposes, cybercriminals, or to install malware on a targeted user’s computer via email or electronic communications scam.
- Clone Phishing – In clone phishing, attackers replicate a previously delivered and legitimate email and replace its content (body of an email) with malicious content.
- Whaling – Whaling is identical to a spear phishing attack but it is directed at senior executives of the companies.
- Link manipulation – In Link manipulation, attackers replicate a trusted website by changing the URL by just a character.
- Filter evasion – The attackers use images instead of phishing text to surpass the anti-phishing software.
- Website forgery – The attackers use JavaScript commands to change the address bar of a website they lead to. It is either done by placing a picture of the valid URL over the website’s address bar or by closing the original address bar and opening a new one with a legitimate URL.
- Covert redirect – It is a subtle method to redirect a user to an illegitimate link by making it appear valid and non-suspicious. Attackers mostly use browser extensions to redirect to fake websites.
- Voice Phishing – In Voice Phishing attacks, attackers use Voice over IP methods claiming that a bank is calling you and asks for the account information.
How to prevent a Phishing attack?
Most of the Phishing attacks are carried out via emails. So, whenever you find something which is too good to be true, be suspicious about it. Most of the times, attackers make an exact replica of a trusted brand that you won’t even doubt about the authenticity of the website. Always, make sure to CHECK the website’s URL. For example, if you regularly shop from ZARA, and you get an exciting email from them leading to a website asking for financial information, watch out for the website URL. It might be like “www.zahra.com” instead of “www.zara.com”.
Precautionary steps to be safe
- Make sure before you click any link.
- Install an Anti-Phishing toolbar.
- Make use of firewalls.
- Be very careful before submitting your personal/bank information online.
- Be aware of Pop-Ups.
- Use Anti-Virus software.
- Check your online accounts regularly.
- Always check the URLs.
